Why There is (Still) a Carrot Boycott in Cuyama Valley
Bolthouse Farms and Grimmway Farms are technically no longer plaintiffs in the lawsuit they launched. But their water war wages on.
Don’t expect to see carrots on Thanksgiving menus in the Cuyama Valley, where residents and small farmers have been boycotting Bolthouse Farms and Grimmway Farms over their outsized water use. They’re still not welcome at the table. Back in September, I wrote about the carrot boycott and the hardball tactics by those big growers that had led to this fight. The water war spilled into the mainstream media this week thanks to an excellent pair of stories by Ian...
CONTINUE READINGHave We Begun the Third Age of Climate Law?
Some thoughts for Environmental History Week.
An international agreement in 1992 committed the world’s nations to addressing climate change but contained few specifics. The US ratified that agreement, but there was little concrete action here through the end of the 20th Century. As this century began, things looked optimistic, with both presidential candidates favoring reductions in carbon emissions. Promptly after taking office, however, George W. Bush reversed himself and fervently embraced fossil fuels. The t...
CONTINUE READINGHow to Get to Zero Emissions at the Ports
A new report by UCLA and UC Berkeley examines policy solutions to accelerate deployment of zero-emission cargo handling equipment at the Ports of Long Beach and Los Angeles.
The Ports of Los Angeles and Long Beach are well on their way toward electrification, but the road to zero emissions is a long one. This new report—A Heavy Lift: Policy Solutions to Accelerate Deployment of Zero-Emission Cargo Handling Equipment at the Ports of Long Beach and Los Angeles and Beyond—surveys the biggest obstacles to speedy electrification and makes some recommendations. The Ports are the largest in the United States, serving as a hub of economic...
CONTINUE READINGClimate Policy in the World’s Fourth Largest Country
In case you’re wondering, that would be Indonesia in terms of population.
Indonesia has the world’s fourth largest population, right after India, China, and the U.S. It has about the same GDP as Spain. Indonesia ranks in the top dozen carbon emitters. It gets relatively attention in the United States. Yet Indonesia’s role in cutting energy emissions is crucial. As an archipelago, Indonesia is at the prey of sea level rise. Jakarta, a city of ten million, is only two feet above sea level. A quarter of the densely populated city could be ...
CONTINUE READINGWho Should Own Our Electric Utilities?
Voters in Maine rejected a ballot initiative to buy out private utilities, but the campaign reflects a growing interest in public power.
This week voters in Maine rejected a ballot measure to implement a public takeover of the state’s two investor-owned utilities. The measure proposed acquiring the two investor-owned utilities that distribute 97% of Maine’s electricity and operating them as a new publicly-owned utility called Pine Tree Power, that would be governed by an elected board. 70% of Mainers voted to reject the measure and 30% supported it (as of this posting). Electric Utility Models ...
CONTINUE READINGEvolving Air Quality Standards
The standards have gotten tougher. Compliance still lags.
The goal of the Clean Air Act is to achieve national ambient air quality standards (NAAQS), with the primary requirement being protection of public health. As our understanding of the health effects of air pollution has improved, there has been a general trend toward tightening the standards. However, it’s very hard to keep track of how the standards have actually evolved. With that in mind, I’ve put together some brief timelines. I am focusing on what are called ...
CONTINUE READINGGetting to Implementation
The Status of Local Climate Action in California
This post is co-authored by CLEE Climate Policy Fellow, Hanna Payne In the arc of climate action, we are firmly in the era of implementation. As climate change accelerates, communities across the state are experiencing the effects of a changing climate. To avoid the worst of these impacts, it is critical that we rapidly implement actions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and build resilience to the effects of a changing climate. Meeting this challenge requires implem...
CONTINUE READINGWhat to watch for, and ignore, at the upcoming climate talks in Dubai
UCLA Law's Mary Nichols, Alex Wang, and Ted Parson preview COP28 in a webinar this Wednesday.
Each year since 1995, the countries of the world have gathered to negotiate what to do about climate change. They do so under the auspices of the Framework Convention on Climate Change, the universally adopted climate change treaty that sets a goal of avoiding dangerous interference with the climate system. Those talks have had ups and downs through the years and have resulted in (among other things) the adoption of the Paris Agreement. Twenty-eight years in...
CONTINUE READINGEnvironmental Policy on the Political Firing Line
“The Empire Strikes Back” or “The Return of the Jedi”? Either is possible on Election Day.
We're now a year away from Election Day, but things are already starting to heat up. And the outcome couldn't be more important. The next election could transform U.S. environmental policy, for better or worse. A GOP trifecta in 2024 would put Trump in the White House with GOP control of Congress. That would be at best a replay of 2017-2019 in terms of environmental policy. There would probably be an even greater impact due to shifts within the GOP. A Democratic trife...
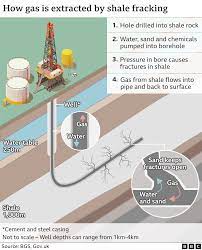
CONTINUE READINGIt’s High Time to Ban “Monster Fracking” in California
Fracking consumes enormous amounts of water, pollutes aquifers & is contrary to our climate goals
Recently, the New York Times published an important and disturbing expose' titled, "'Monster Fracks' Are Getting Far Bigger. And Far Thirstier." The Times article focuses on the alarming intersection of three current environmental crises--water supply shortages, groundwater contamination, and excessive greenhouse gas emission levels--that threaten California and other states across the nation. Fracking (the shorthand term for "hydraulic fracturing") is a p...
CONTINUE READING