Climate Change
Does the Law Require Cost-Benefit Analysis?
According to the D.C. Circuit, the answer is no.
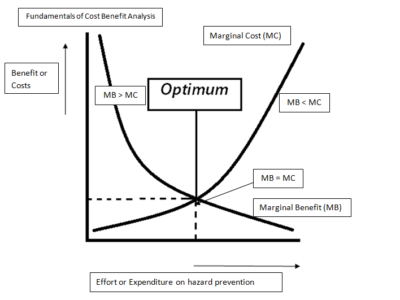
Putting aside the particulars of the case, it seems wrong to apply the same standard (monetized cost-benefit analysis) to every provision in environmental law. These provisions have different language, reflecting differences in congressional priorities. Some provisions, for instance, may be designed push industry to find innovative solutions; others may reflect Congress’s value judgments or a desire to limit EPA’s discretion. We shouldn’t assume that the myriad differences in statutory language are irrelevant and that Congress wanted agencies to adopt the same method of making decisions in every case.
CONTINUE READINGThe Emperor’s New Endangerment Theory (Wrap-Up)
Trump’s EPA says carbon emissions from U.S. power plants are too insignificant to regulate.
U.S. power plants emit 1.5 billion tons of carbon dioxide a year, a little less than the entire country of Russia. The Trump Administration is proposing to end all regulation of carbon emissions by power plants, on the theory that these emissions should be considered insignificant. They have some complicated legal arguments , but the arguments break down the more closely you look at them.
CONTINUE READINGThe Emperor’s New Endangerment Theory (Part III)
How did EPA get to the absurd conclusion that 1.5 billion tons of carbon emissions aren’t significant? Well might you ask.
There is a very good chance that a court would strike down a EPA’s current finding that carbon emissions from the U.S. power sector are too insignificant to regulate. EPA’s effort to explain its ultimate conclusion rests on a hodgepodge of poorly analyzed considerations, which obviously have been reverse engineered to lead to EPA’s preferred conclusion.
CONTINUE READINGThe Emperor’s New Endangerment Theory (Part II)
To justify a decision not to regulate CO2 from power plants, EPA had to twist statutory language beyond all recognition.
According to EPA, carbon emissions from the U.S. power sector are too insignificant to warrant regulation. This is a bizarre conclusion: U.S. power sector’s emissions are around 6.5 billion tons, just below Russia’s total emissions from all sectors. To reach this conclusion, EPA has proposed a novel reading of the Clean Air Act. In EPA’s view, before it could regulate those emissions, it would first have to make a formal finding that they “cause or significantly contribute” to climate change, and (2) that this has to be judged on the basis of the sector’s percentage of total global carbon emissions. The statute doesn’t say either of those things.
CONTINUE READINGThe Emperor’s New Endangerment Theory (Part I)
EPA says the electricity sector’s climate impacts aren’t significant. Really??
EPA has proposed a novel reading of the Clean Air Act (CAA) that would foreclose any regulation of CO2 emissions from power plants. EPA’s core argument is that the statute requires it to determine whether an industry’s emissions “cause or contribute significantly” to climate change and that the industry’s carbon emissions don’t meet that standard. …
Continue reading “The Emperor’s New Endangerment Theory (Part I)”
CONTINUE READINGLast Year’s Climate Bond May Not Be What You Thought
While investing in important adaptation and resilience measures, Proposition 4 does less to create new clean energy infrastructure investments
Last year, legislators passed, the governor signed, and California voters approved, a ten billion dollar climate bond (the Safe Drinking Water, Wildfire Prevention, Drought Preparedness, and Clean Air Bond Act of 2024, SB 867 (Allen), which appeared on the November ballot as Proposition 4). While the bond act’s full title largely tells the story of …
Continue reading “Last Year’s Climate Bond May Not Be What You Thought”
CONTINUE READINGAbundance and the Seven County case
The Court’s decision will facilitate fossil fuel projects much more than clean energy
I’ve seen some posts on the social media site formally known as Twitter arguing that the Seven County case is a win for an abundance-focused policy – in that it will facilitate more construction of infrastructure by eliminating or reducing environmental reviews. I think that statement is somewhat accurate in general. But I think it is …
Continue reading “Abundance and the Seven County case”
CONTINUE READINGImplications of the Seven County Decision
Possible limitations on NEPA analysis for climate effects and indirect effects
This is the third in our series of posts on the Seven County case. The first post was here, summarizing the key points of the opinion. The second post is here, providing our assessment of the analysis in the opinion. In this third post, we discuss the implications of the case for what have been …
Continue reading “Implications of the Seven County Decision”
CONTINUE READINGBrazil Steps Ahead of the U.S. on Climate Policy
A new emissions trading system is a major step for Brazilian climate policy.
Hopefully, Brazil’s actions will encourage other countries, particularly in South America, to take similar actions. The EU and California have been leaders in this arena, but carbon trading systems are now beginning to get traction outside of the developed world in China and now Brazil. That’s an encouraging sign.
CONTINUE READINGDefunding the Energy Transition
The President Proposes Deep Cuts to Climate and Clean Energy Spending for FY 2026
On May 2nd, the White House released what is generally referred to as a “skinny” budget request outlining priorities for discretionary spending for fiscal year 2026. A full federal budget proposal is expected later this month. The “skinny” budget contains, by the White House’s calculations, $163 billion in non-defense discretionary spending cuts, which it argues …
Continue reading “Defunding the Energy Transition”
CONTINUE READING