Environmental Science
Gene Drives, Biodiversity Conservation, International Law, and Emerging Politics
My latest article is published by Global Environmental Politics
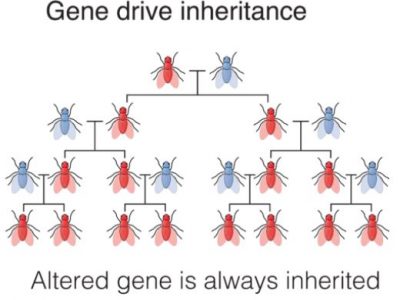
A set of new biotechnologies are being developed that will force many of us, especially those concerned about biodiversity loss, to re-examine how we understand the relationship between biotechnology and conservation. These are “gene drives,” which would be used to genetically modify, reduce, or eliminate populations of species. My paper “Governing New Biotechnologies for Biodiversity …
Continue reading “Gene Drives, Biodiversity Conservation, International Law, and Emerging Politics”
CONTINUE READINGEnforcing NEPA’s Forgotten Mandate
The courts have failed to enforce a core requirement of NEPA. That leaves the White House.
The Democrats have adopted an ambitious platform for environmental protection, full of innovative legislative initiatives. Here’s another idea Biden and Harris should consider, making use of the oldest of the modern environmental statutes. The National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) is best known for requiring environmental impact statements. While they have enforced that requirement, the courts …
Continue reading “Enforcing NEPA’s Forgotten Mandate”
CONTINUE READINGUCLA Law Faculty Weigh In on Solar Geoengineering Experiment at Harvard
How to engage the public when everyone on Earth is a stakeholder?
It’s been a surprisingly busy year for solar geoengineering research. In late December, Congress appropriated $4 million to NOAA to study the influence of atmospheric aerosols on climate, with an eye on assessing “solar climate interventions.” In March, Australian scientists ran a trial of a cloud-seeding technology on the Great Barrier Reef that may …
Continue reading “UCLA Law Faculty Weigh In on Solar Geoengineering Experiment at Harvard”
CONTINUE READINGThe Danger of Climate Change Deadlines
Essential targets set by some of the world’s leading climate scientists and policymakers just passed. Now what?
Seven prominent figures in the global climate change policy discourse published an opinion essay in Nature. In “Three years to safeguard our climate,” they set a deadline for key targets to be met in order to stay on track to meet the Paris Agreement’s global warming goals. The notable thing is that the essay was …
Continue reading “The Danger of Climate Change Deadlines”
CONTINUE READINGThe Scourge of ERRD-16
Evident-Resistant Reasoning DIsorder can strike without warning.
A stubborn disagreement. A misguided tweet or facebook post. A lame remark. Those things can be normal behaviors. But they could be signs of something much more serious: a syndrome called Evidence-Resistant Reasoning Disorder or ERRD-16. This disorder has expanded explosively since a mutated form was introduced by a super-spreader in 2016. This super-spreader is …
Continue reading “The Scourge of ERRD-16”
CONTINUE READINGEnvironmentalists v. Cost-Benefit Analysis: What Does the Future Hold?
For now, at least, environmentalists and economists are aligned in criticizing Trump’s rollbacks. Will this alliance last?
If it’s true that “the enemy of my enemy is my friend,” environmentalists might want to take another look at cost-benefit analysis. The Trump Administration is certainly doing its best to gut economic analysis of its rollbacks. Both economists and environmentalists are resisting. Is this an alliance of convenience or will it be the start …
Continue reading “Environmentalists v. Cost-Benefit Analysis: What Does the Future Hold?”
CONTINUE READINGA New Report on Governing Climate Geoengineering
I suggest steps toward global governance of carbon dioxide removal and solar geoengineering
A new report on the governance of climate geoengineering — that is, carbon dioxide removal (CDR) and solar geoengineering (or solar radiation modification, SRM) — has been released. International Governance Issues on Climate Engineering: Information for Policymakers was coordinated and issued by the International Risk Governance Center, edited by IRGC’s Marie-Valentine Florin, and commissioned by the …
Continue reading “A New Report on Governing Climate Geoengineering”
CONTINUE READING(Still More) Bad News on the Doorstep
New Reports Document Accelerating Wildlife Extinctions, Global Deforestation Trends
While public attention in recent weeks and months has understandably focused on the COVID-19 pandemic and the racial justice shockwaves triggered by George Floyd’s tragic death, another disaster continues apace. This week the New York Times published two alarming stories documenting the accelerating decline of our global environment. The first, entitled “Extinctions Are Accelerating, Threatening …
Continue reading “(Still More) Bad News on the Doorstep”
CONTINUE READINGTrees Will *Not* Solve Climate Change
The authors of a controversial, influential paper backtrack — again
Last summer, I pointed to a then-new paper in Science that concluded that planting trees could remove two-thirds of historical anthropogenic carbon dioxide emissions from the atmosphere at very low costs. At the time, I characterized the claims in it and the associated media communications as “misleading, if not false, as well as potentially dangerous.” …
Continue reading “Trees Will *Not* Solve Climate Change”
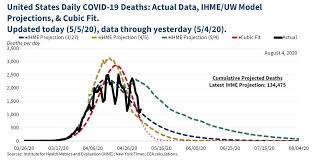
CONTINUE READINGUsing and Abusing Models: Lessons from COVID-19
We’ve seen some great examples of how NOT to deal with models.
Models have figured heavily in government responses to the coronavirus. This has given us the opportunity for a real-time lesson in the uses of models. In the process, we’ve learned some important lessons in how to best make use of models — and equally importantly, in how not to use them. That’s directly relevant to …
Continue reading “Using and Abusing Models: Lessons from COVID-19”
CONTINUE READING